 3 Ways to Treat a Child's Hernia - wikiHow Mom
3 Ways to Treat a Child's Hernia - wikiHow MomLoading...Information about the Coronavirus Novel 2019. Information about coronavirus 2019 (COVID-19). Hiatal Hernia What is a hial hernia? A hernia is when part of an organ passes through an opening in the muscle wall around it. In a hiatal hernia, part of your stomach pushes towards an opening (the hiatus) in your diaphragm. The diaphragm is the muscle between the stomach and the chest. In most cases, your food pipe ( esophagus) passes through the hiatus and joins your stomach. But with a hiatal hernia, the upper part of your stomach moves through that opening in your chest. The upper part of your stomach pinches. Stomacal acid can retrocede (reflux) through the opening. This can cause heart acidity and other symptoms. There are 2 types of hiatal hernias: slider and paraesophageal. Hial hernia This type of hernia: It is more commonIt happens when part of the stomach, and the place where the stomach and esophagus are located, slipping into your chest through the opening (hiatus) Paraesophageal hernia This type of hernia: It is less common but can be more serious It happens when part of your stomach pushes up through the opening (hiatus) in your chest and is next to your esophagus What causes a hial hernia? The experts don't know what causes hernias hiathales. Some causes may include: TosingVomitingStraining while having a bowel movement Pregnancy Obesity Who is at risk of a hial hernia? You may be at greater risk of a hiatal hernia if you: They are 50 years or older Are overweight or obese What are the symptoms of a hial hernia? In many cases, a hiatal hernia has no symptoms. Some people have symptoms. These may include:BurpingFeeling nauseousVomitingBackflow (reflux) of acid or stomach content in the esophagus or throatHeartburnRegurgitationBlue swallow Paraesophageal hernias may have more severe symptoms. These may include:Having trouble swallowing sometimes, more often with solid foods Feeling full after eating only a small amount of meatBelly (abdominal) or chest pain Abdominal bleeding Blood loss (anemia)In some cases a paraesophageal hernia may lead to a medical emergency. The stomach or abdominal organs can spin or spin, causing very bad pain. There is a danger that the blood supply of the stomach can be cut (shortening). It's an emergency. You probably need surgery right away. Symptoms of a hiatal hernia may look like other health problems. Always consult your healthcare provider to be sure. How is a hial hernia diagnosed? Your healthcare provider will give you a physical exam. They'll look at your past health. You may also have tests that include: chest X-ray. This can prove you have a hial hernia. Upper endoscopy, also called EGD (esophagogastroduodenoscopy). This test examines the lining of your food pipe ( esophagus), stomach and the first part of your small intestine (the duodenum). Use a thin light tube, called a endoscope. The tube has a camera at one end. The tube gets in the mouth and throat. Then he enters his esophagus, stomach, and duodenum. Your healthcare provider can see the inside of these organs. Upper GI series (gastrointestinal) or barium swallow. This test examines the organs at the top of your digestive system. Check your food pipe ( esophagus), stomach and the first part of your small intestine (the duodenum). A metallic liquid called a barium will be swallowed. The barium covers the organs so they can be seen in an X-ray. Esophageal maniometry. This test checks the strength of the esophagus muscles. You can see if you have any problems with reflux or ingestion. A small tube gets into your nose, then lower your throat in your esophagus. This measures the pressure that your esophagus muscles do at rest. How is a hial hernia treated? Treatment will depend on your symptoms, age, and general health. It will also depend on the severity of the condition. In most cases you will not need treatment. But you may need medical care if your hernia: It is more difficult because of severe gastroesophageal reflux disease (inflammation)Your healthcare provider may suggest medicines for:Stamacal acid (ancids)Reduce the amount of stomach acid (an acids)Reduce the amount of acidH is at risk of being twisted so much that the blood supply is cut to your stomach (sphere) In severe cases surgery may also be needed to:Make Your Hernia Smaller Leave the loss of blood flow to your stomach (stribilization) by closing the opening on your diaphragm What are the possible complications of a hial hernia? In most cases a hial hernia will not lead to other health problems. In some cases it may cause other problems such as:Severe GERD (gastroesophageal reflux disease)Pungal or pneumonia problems because the stomach content has moved to your esophagus and to one or both lungs. Hernia strangulation, cutting blood flow to your stomach (medical emergency) What can I do to prevent a hial hernia? Health experts don't know what causes hiatal hernias. They don't know how to stop them from happening. Living with a hiatal herniaFollow your health care provider's advice to treat and manage your hiatal hernia. You may need to make some lifestyle changes, such as: Losing weight if you are overweight or obese Do not eat for 3 to 4 hours before going to bed Do not bend right after eating When should I call my healthcare provider? Call your healthcare provider if your symptoms come back after your treatment has stopped them. Let them know if the symptoms get worse or have new symptoms. Key points on hial hernia A hiatal hernia is when part of your stomach pushes towards an opening (the hiatus) on your diaphragm. There are 2 types of hiatal hernias: slider and paraesophageal. Paraesophageal hernias are less common but can be more severe. You may need surgery. The experts don't know what causes hernias hiathales. In most cases there are no symptoms. In most cases no medical care is needed. Next steps Tips to help you get the most out of a visit to your healthcare provider: Know the reason for your visit and what you want to happen. Before your visit, write questions you want to answer. Bring someone with you to help you ask questions and remember what your provider tells you. In the visit, type the name of a new diagnosis, and any new medication, treatment or test. Also write any new instruction your provider gives you. Know why a new medication or treatment is prescribed, and how it will help you. He also knows what side effects are. Ask if your condition can be treated in other ways. Know why a test or procedure is recommended and what the results can mean. Know what to expect if you do not take the medication or have the test or procedure. If you have a follow-up appointment, type the date, time and purpose for that visit. You know how you can contact your provider if you have questions. Related Issues© 2021 Stanford Children's HealthAboutConnectFindAlsoInform us on:
Accessibility Links Search ModesSearch Resultssearch.proquest.com/openview/9ccc641deb1f1e87aaa0ff...Hyatal hernia symptoms; hiatal hernia symptoms and ... Clinical Significance of Hiatal Hernia - NCBI - Hernia NIHiatal - The Hernia of PortlandHiatal (B stomach Hernia) - UpToDateGuidelines for the Management of Hiatal Hernia - A SAGES...Hiatus Hernia. The acid reflux causes hernia hiato. Links for patients

Surgery for Hernias in Children | Spectrum Health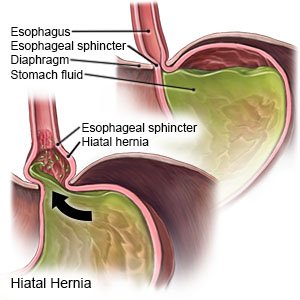
Hiatal Hernia in Children - What You Need to Know
Hernia repair: Care for your child after the operation
Cincinnati Ohio Hiatal Hernia Treatment and Relief | Symptoms | Hiatus
Hiatal Hernia or Hiatus Hernia|Causes|Risk Factors|Signs|Symptoms|Tests|Treatment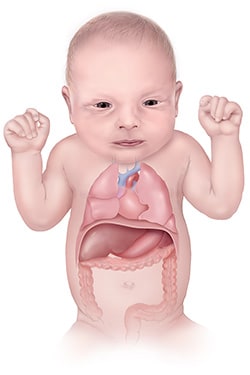
Facts about Diaphragmatic Hernia | CDC
Hiatus Hernia: March 2012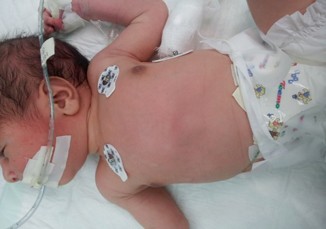
Congenital Diaphragmatic Hernia | SpringerLink
What to Know About Hiatal Hernias - University Health News
Location of trocars for laparoscopic approach to hiatal hernia in... | Download Scientific Diagram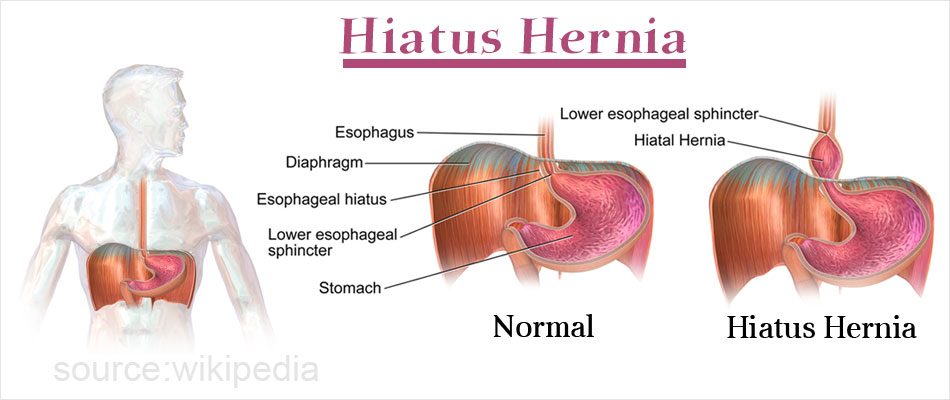
Hiatus Hernia - Types, Causes, Symptoms, Complications, Diagnosis, Treatment, Prevention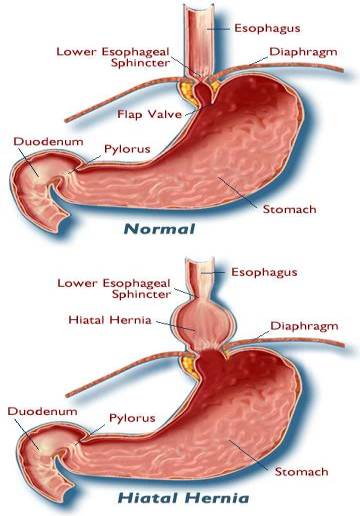
Midwest Gi - Gastroenterlogy Specialists in Lee's Summit Mo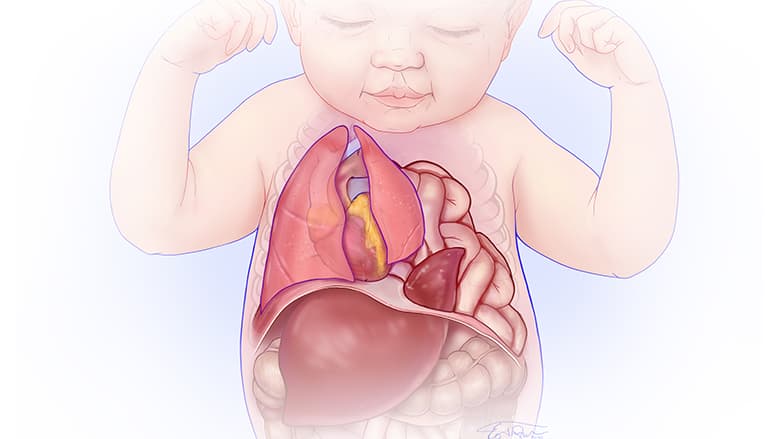
Congenital Diaphragmatic Hernia (CDH) | Children's Hospital of Philadelphia
Dedicated to the mission of bringing free or low-cost educational materials and information to the global ultrasound community.
Figure 1 from Hiatal hernia in pediatric patients: laparoscopic versus open approaches | Semantic Scholar
Prenatal diagnosis of congenital paraesophageal hiatal hernia - ScienceDirect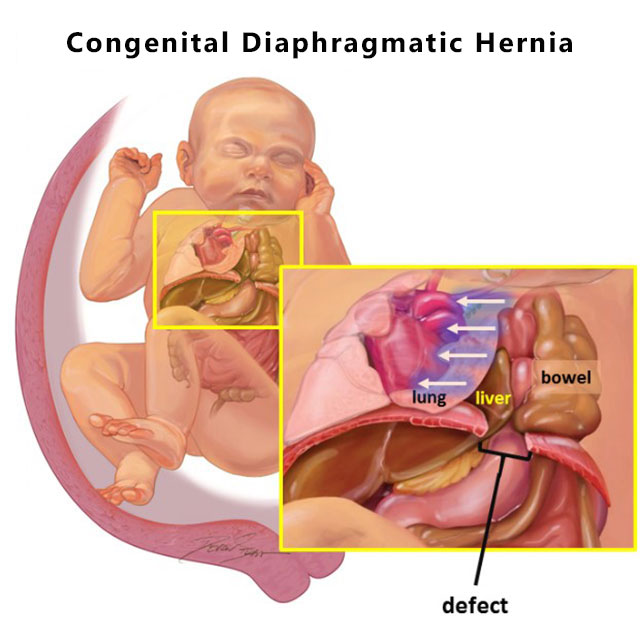
Congenital Diaphragmatic Hernia | Johns Hopkins Medicine
Hiatus Hernia - Gastrointestinal Disorders - MSD Manual Professional Edition/hiatal-hernia-causes-5ae0baf7c5542e0036f06541.png)
Hiatal Hernia: Causes and Risk Factors
Hiatal Hernia | South Coast Specialty Surgery Center
Barium metal showing child hiatus hernia. | Download Scientific Diagram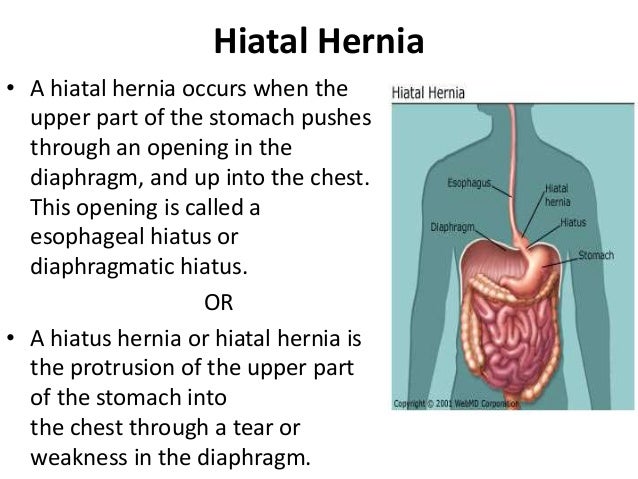
Hiatal hernia
Mohajerzadeh
Atypical presentations of hiatal hernia in two pediatric patients Ajij M, Shambhavi, Gupta S - Niger J Gen Pract
Guidelines for the Management of Hiatal Hernia - A SAGES Publication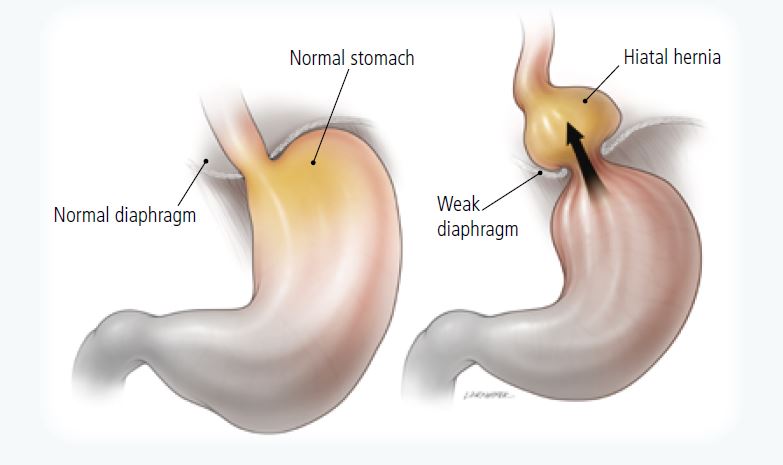
Hernia - Harvard Health
a PA view of a hiatal hernia (arrow). b Lateral view of a hiatal hernia... | Download Scientific Diagram
Hiatal Hernia Adjustment | Video Interview | Nutrition by Erin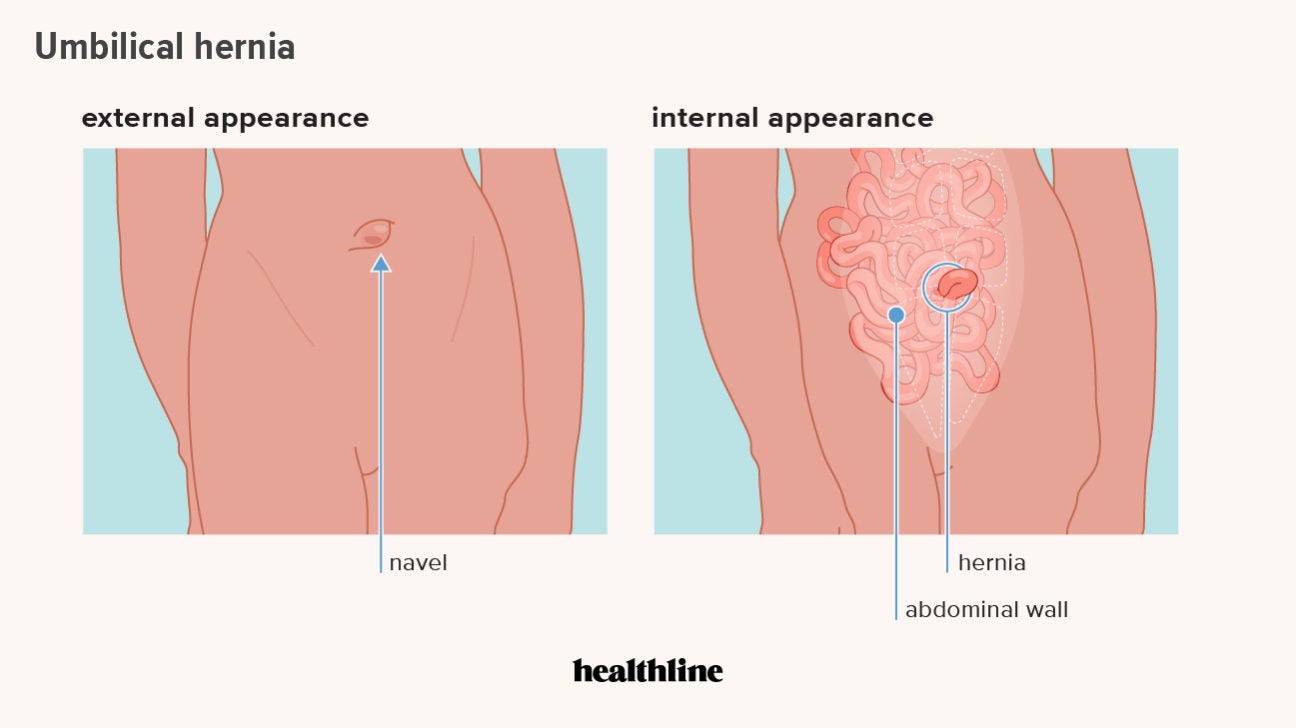
Hernia Pictures of 6 Common Types
Hernia In Premature Baby Boy - Newborn baby
Types of Hernias Found in Preemies | LoveToKnow
Congenital Diaphragmatic Hernia (CDH): About, Diagnosis & Treatment | SSM Health
Types of Hernia | Everyday Health
Hernia: Types, Causes, Symptoms, Treatment, Risk Factors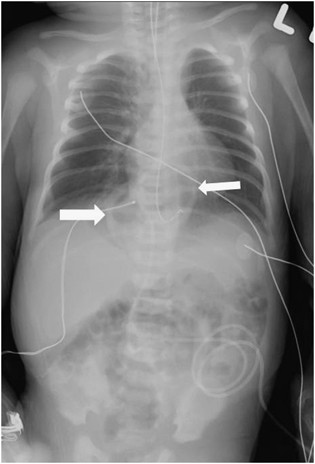
Neonatal marfan syndrome with hiatus hernia and intrathoracic stomach | Journal of Perinatology![PDF] Ultrasound Diagnosis of Gastroesophageal Reflux and Hiatal Hernia in Infants and Young Children | Semantic Scholar PDF] Ultrasound Diagnosis of Gastroesophageal Reflux and Hiatal Hernia in Infants and Young Children | Semantic Scholar](https://d3i71xaburhd42.cloudfront.net/44465e8a2330a5ce70ff1f152d44149a9832ed3c/4-Figure3-1.png)
PDF] Ultrasound Diagnosis of Gastroesophageal Reflux and Hiatal Hernia in Infants and Young Children | Semantic Scholar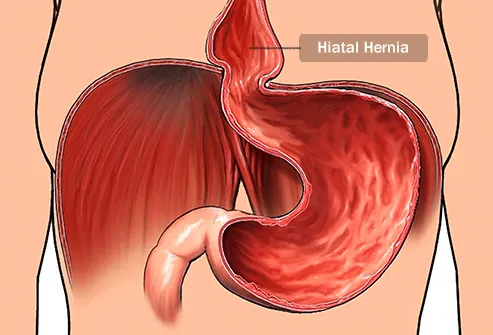
Visual Guide To Hernias
Acid Reflux in Infants: Causes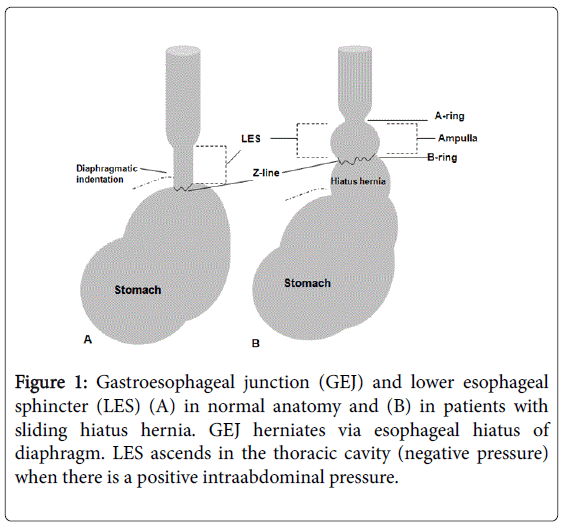
Impact of Hiatal Hernia on Pediatric Gastroesophageal Reflux Disease | OMICS International
3 Ways to Treat a Child's Hernia - wikiHow Mom
 3 Ways to Treat a Child's Hernia - wikiHow Mom
3 Ways to Treat a Child's Hernia - wikiHow Mom

















/hiatal-hernia-causes-5ae0baf7c5542e0036f06541.png)














![PDF] Ultrasound Diagnosis of Gastroesophageal Reflux and Hiatal Hernia in Infants and Young Children | Semantic Scholar PDF] Ultrasound Diagnosis of Gastroesophageal Reflux and Hiatal Hernia in Infants and Young Children | Semantic Scholar](https://d3i71xaburhd42.cloudfront.net/44465e8a2330a5ce70ff1f152d44149a9832ed3c/4-Figure3-1.png)




Posting Komentar untuk "hiatal hernia in infants"